Novi Pazar
Novi Pazar
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Novi Pazar Град Нови Пазар | ||
|---|---|---|
City | ||
| City of Novi Pazar | ||
       From top: City panorama at night, Monastery The Tracts of Saint George, The Sopoćani monastery, Novi Pazar Fortress, Altun-Alem Mosque, International University of Novi Pazar, Church of the Holy Apostles Peter and Paul, Ras | ||
| ||
 Location of the city of Novi Pazar within Serbia | ||
| Coordinates: 43°09′N 20°31′E / 43.150°N 20.517°E / 43.150; 20.517Coordinates: 43°09′N 20°31′E / 43.150°N 20.517°E / 43.150; 20.517 | ||
| Country | ||
| Region | Šumadija and Western Serbia | |
| District | Raška | |
| Founded | 1461 | |
| Settlements | 100 | |
| Government | ||
| • Mayor | Nedim Krnjoejalac (SDP) | |
| Area [1] | ||
| Area rank | 31st in Serbia | |
| • Urban | 15.34 km2 (5.92 sq mi) | |
| • Administrative | 742 km2 (286 sq mi) | |
| Elevation | 477 m (1,565 ft) | |
| Population (2011 census)[2] | ||
| • Rank | 14th in Serbia | |
| • Urban | 66,527 | |
| • Urban density | 4,300/km2 (11,000/sq mi) | |
| • Administrative | 100,410 | |
| • Administrative density | 140/km2 (350/sq mi) | |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) | |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) | |
| Postal code | 36300 36302 36303 36316 36318 36319 36322 | |
| Area code | +381(0)20 | |
| ISO 3166 code | SRB | |
| Car plates | NP | |
| Climate | Cfb | |
| Website | www.novipazar.rs | |
Novi Pazar (Serbian Cyrillic: Нови Пазар, lit. "New Bazaar" pronounced [nôʋiː pǎzaːr]) is a city located in the Raška District of southwestern Serbia. As of the 2011 census, the urban area has 66,527 inhabitants, while the city administrative area has 100,410 inhabitants.[3] The city is the cultural center of the Bosniaks in Serbia and the historical region of Sandžak.[4] A multicultural area of Muslims and Orthodox Christians, many monuments of both religions, like the Altun-Alem Mosque and the Church of the Holy Apostles Peter and Paul, are found in the region.
Contents
1 Name
2 Geography
2.1 Climate
3 History
4 Demographics
4.1 Ethnic composition
5 Settlements
6 Politics
7 Economy
8 Society and culture
8.1 Monuments
8.2 Education
8.3 Sport
9 Gallery
10 Notable residents
11 References
12 External links
Name[edit]
During the 14th century under the old Serbian fortress of Stari Ras, an important market-place named Trgovište started to develop. By the middle of the 15th century, in the time of the final Ottoman Empire conquest of Old Serbia, another market-place was developing some 11 km to the east. The older place became known as Staro Trgovište (Old Trgovište, Turkish: Eski Pazar) and the younger as Novo Trgovište (New Trgovište, Turkish: Yeni Pazar). The latter developed into the modern city of Novi Pazar.
The name Novi Pazar (meaning "New Bazaar") was derived from the Serbian name Novo Trgovište, via the Turkish name Yeni Pazar, which is itself derived from bazaar (from Persian .mw-parser-output .noitalicfont-style:normal
بازار (bāzār), meaning 'market'; from Pahlavi
بهاچار (bahā-chār), meaning 'place of prices').[5] It is still known as Yeni Pazar in modern-day Turkey.
Geography[edit]
Novi Pazar is located in the valleys of the Jošanica, Raška, Deževska, and Ljudska rivers. It lies at an elevation of 496m, in the southeast Sandžak region. The city is surrounded by the Golija and Rogozna mountains, and the Pešter plateau lies to the west. The total area of the city administrative area is 742 km². It contains 100 settlements, mostly small and spread over hills and mountains surrounding the city. The largest village is Mur, with over 3000 residents.[citation needed]
Climate[edit]
Novi Pazar has a humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification: Dfb) typical of the hilly Sandžak region, though significantly warmer than the neighboring town of Sjenica.
| Climate data for Novi Pazar | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 2.7 (36.9) | 5.6 (42.1) | 11.1 (52.0) | 15.5 (59.9) | 20.1 (68.2) | 23.6 (74.5) | 26.1 (79.0) | 26.4 (79.5) | 22.7 (72.9) | 16.5 (61.7) | 8.8 (47.8) | 4.3 (39.7) | 15.3 (59.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −0.6 (30.9) | 1.6 (34.9) | 6.3 (43.3) | 10.2 (50.4) | 14.6 (58.3) | 18.0 (64.4) | 20.1 (68.2) | 20.1 (68.2) | 16.7 (62.1) | 11.4 (52.5) | 5.2 (41.4) | 1.2 (34.2) | 10.4 (50.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −3.9 (25.0) | −2.4 (27.7) | 1.5 (34.7) | 5.0 (41.0) | 9.2 (48.6) | 12.5 (54.5) | 14.1 (57.4) | 13.8 (56.8) | 10.7 (51.3) | 6.4 (43.5) | 1.6 (34.9) | −1.8 (28.8) | 5.6 (42.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 71 (2.8) | 64 (2.5) | 66 (2.6) | 74 (2.9) | 92 (3.6) | 78 (3.1) | 68 (2.7) | 62 (2.4) | 69 (2.7) | 80 (3.1) | 93 (3.7) | 83 (3.3) | 900 (35.4) |
| Source: [6] | |||||||||||||
History[edit]

Church of the Holy Apostles Peter and Paul from the 9th century
One of the oldest monuments of the area is the Church of the Holy Apostles Peter and Paul first built in the Roman era. The capital city of the Principality of Serbia, Ras, which was ruled by the Vlastimirović dynasty from 768 to 980, was near the modern city and has been designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site.[citation needed]
In the next centuries, the region of modern Novi Pazar served as the principal province of the Serbian realm. It was an administrative division, usually under the direct rule of the monarch and sometimes as an appanage. It was the crownland, seat or appanage of various Serbian states throughout the Middle Ages, including the Serbian Kingdom (1217-1345) and the Serbian Empire (1345-1371). In 1427, the region and the remnant of Ras, as part of the Serbian Despotate, was ruled by Serbian despot Đurađ Branković. One of the markets was called "despotov trg" (Despot's square).[7] In 1439, the region was captured by the Ottoman Empire, but was reconquered by the Serbian Despotate in 1444. In the summer of 1455, the Ottomans conquered the region again, and named the settlement of Trgovište Eski Bazar (Old Market). Novi Pazar was formally founded as a city in its own right in 1461 by Ottoman general Isa-Beg Ishaković, the Bosnian governor of the district (sanjak) who also founded Sarajevo.[8] Ishaković decided to establish a new town on the area of Trgovište as an urban center between Raška and Jošanica, where at first he built a mosque, a public bath, a marketplace, a hostel, and a compound.[citation needed]
It was the chief town of the Ras province (vilayet) until its disestablishment in 1463, when it became part of the Jeleč Vilayet. The first written document which mentions Novi Pazar dates from the 15th century, and describes the decision of the Republic of Ragusa to appoint a consul there. The town was well developed by this time, being at the intersection of important routes leading to Dubrovnik, Niš, Sofia, Constantinople, Salonica, Sarajevo, Belgrade and Budapest. The town also remained the capital of the Sanjak of Novi Pazar, which continued until the 20th century as a constitutive unit of Bosnia Eyalet. The sanjak was occupied and administered by Austria-Hungary from 1878. In 1908 it was returned to the Ottoman Empire as part of the Kosovo Vilayet, but taken over by the Kingdom of Serbia in 1912, during the First Balkan War.[citation needed]
The area has traditionally had a large number of Albanians and Muslim Slavs with a different culture from the Orthodox Serbs.[9] A contemporary report stated that when the Serb forces entered the Sandjak of Novi Pazar, they "pacified" the Albanians.[10] In 1913, Novi Pazar officially became part of the Kingdom of Serbia, and as such, became part of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in 1918. From 1929 to 1941, Novi Pazar was part of the Zeta Banovina of the Yugoslavia.[citation needed]
In the Battle for Novi Pazar, fought at the end of 1941 during the Second World War, the Chetniks, initially supported by the Partisans, unsuccessfully tried to capture the city.[citation needed] Following the overthrow of Slobodan Milošević on 5 October 2000, newly elected Prime Minister of Serbia Zoran Đinđić made considerable efforts to help economically the whole area of Novi Pazar. Also, with the help of Đinđić, the International University of Novi Pazar was founded in 2002. He made close relations with the leaders of Bosniaks, as part of his wider plan to reform Serbia.[11] Twelve years following his assassination, the Novi Pazar Assembly decided to rename one street in his name.[12]
Demographics[edit]
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
| 1948 | 44,020 | — |
| 1953 | 50,189 | +2.66% |
| 1961 | 58,776 | +1.99% |
| 1971 | 64,326 | +0.91% |
| 1981 | 74,000 | +1.41% |
| 1991 | 85,249 | +1.43% |
| 2002 | 85,996 | +0.08% |
| 2011 | 100,410 | +1.74% |
| Source: [13] | ||

Prvomajska Street in Novi Pazar.
According to the last official census done in 2011, the city of Novi Pazar has 100,410 inhabitants, while the city itself has 68,749 inhabitants. A total of 68.47% of population live in urban area of the city. The population density is 135.32 inhabitants per square kilometer.[14]
Novi Pazar has 23,022 households with 4,36 members on average; the number of homes is 28,688.[15]
Religion structure in the city of Novi Pazar is predominantly Muslim (82,710), with Serbian Orthodox (16,051), Atheists (71), Catholics (51), and other minority groups.[16] Most of the population speaks either Bosnian (74,501) or Serbian (23,406).[16]
The composition of population by sex and average age:[16]
- Male - 49,984 (32.90 years) and
- Female - 50,426 (34.14 years).
A total of 33,583 citizens (older than 15 years) have secondary education (44.41%), while the 7,351 citizens have higher education (9.72%). Of those with higher education, 5,005 (6.62%) have university education.[17]
Ethnic composition[edit]
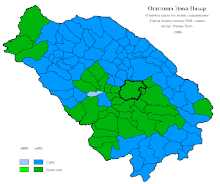
Ethnic composition of Novi Pazar settlements (2002 census)
From the 15th century to the Balkan Wars, Novi Pazar was the capital of the sanjak of Novi Pazar. Typically, like other centres of the wider area, its composition was multiethnic, with Albanians, Serbs and Slavic-speaking Muslims as the main communities.[18] The Ottoman travel writer Evliya Celebi noted that it was one of the most populated towns in the Balkans in the 17th century. Serbs also lived in the city until WWII[19] when the entire Serb population of Novi Pazar - 521 individuals, were imprisoned, sent to the concentration camp Staro Sajmište and killed during the rule of Balli Kombëtar.[20]
The ethnic composition of the city administrative area:[21][22]
| Ethnic group | Population 1953[23] | Population 1961[24] | Population 1971[25] | Population 1981[26] | Population 1991[27] | Population 2002[28] | Population 2011[3] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Bosniaks | - | - | - | - | - | 65,593 | 77,443 |
Serbs | 25,177 | 27,933 | 25,076 | 21,834 | 19,064 | 17,599 | 16,234 |
Muslims | - | 23,250 | 37,140 | 49,769 | 64,251 | 1,599 | 4,102 |
Roma | - | 37 | 210 | 444 | 334 | 69 | 566 |
Gorani | - | - | - | - | - | 15 | 246 |
Albanians | 144 | 126 | 307 | 233 | 209 | 129 | 202 |
Montenegrins | 174 | 543 | 359 | 295 | 232 | 109 | 44 |
Yugoslavs | 13,564 | 1,261 | 183 | 931 | 700 | 136 | 67 |
Turks | 11,009 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Others | 263 | 5,627 | 1,057 | 494 | 459 | 747 | 1,506 |
Total | 50,331 | 58,777 | 64,326 | 74,000 | 85,249 | 85,996 | 100,410 |
Ethnic composition of the urban area of the city:
| Ethnic group | Population 1948[29] | Population 1953[23] | Population 1981[26] | Population 1991[27] | Population 2002[28] | Population 2011[3] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Bosniaks/Muslims | 1,085 | - | 32,798 | 43,774 | 47,243 | 58,252 |
Serbs | 10,678 | 3,466 | 6,689 | 6,698 | 6,724 | 6,576 |
Gorani | - | - | - | - | - | 240 |
Albanians | - | 134 | 208 | 172 | 120 | 162 |
Yugoslavs | - | 5,944 | 848 | 570 | 105 | 64 |
Turks | - | 4,280 | - | - | - | - |
Montenegrins | - | 145 | 246 | 190 | 93 | 39 |
| Others | 229 | 135 | 310 | 345 | 1,541 | 3,410 |
Total | 11,992 | 14,104 | 41,099 | 51,749 | 54,604 | 68,749 |
Settlements[edit]
This section needs to be updated. (January 2015) |
Aside from the urban area of Novi Pazar (54,604), the city administrative area includes the following settlements, with population from the 2002 census:
Aluloviće (362)
Bajevica (563)
Banja (466)
Bare (36)
Batnjik (58)
Bekova (116)
Bele Vode (872)
Boturovina (218)
Brđani (195)
Brestovo (5)
Čašić Dolac (76)
Cokoviće (20)
Deževa (238)
Dojinoviće (120)
Dolac (87)
Doljani (89)
Dragočevo (112)
Dramiće (80)
Golice (64)
Gornja Tušimlja (33)
Goševo (50)
Gračane (28)
Građanoviće (19)
Grubetiće (259)
Hotkovo (193)
Ivanča (813)
Izbice (1,949)
Jablanica (27)
Janča (332)
Javor (18)
Jova (21)
Kašalj (35)
Koprivnica (12)
Kosuriće (125)
Kovačevo (243)
Kožlje (618)
Kruševo (486)
Kuzmičevo (133)
Leča (319)
Lopužnje (70)
Lukare (489)
Lukarsko Goševo (850)
Lukocrevo (186)
Miščiće (231)
Muhovo (545)
Mur (3,407)
Negotinac (26)
Odojeviće (50)
Oholje (179)
Okose (36)
Osaonica (284)
Osoje (966)
Paralovo (982)
Pasji Potok (42)
Pavlje (178)
Pilareta (26)
Pobrđe (2,176)
Polokce (117)
Pope (83)
Postenje (3,471)
Požega (523)
Požežina (251)
Prćenova (159)
Pusta Tušimlja (53)
Pustovlah (28)
Radaljica (152)
Rajčinoviće (537)
Rajčinovićka Trnava (208)
Rajetiće (63)
Rajkoviće (29)
Rakovac (21)
Rast (51)
Šaronje (398)
Šavci (247)
Sebečevo (897)
Sitniče (778)
Skukovo (23)
Slatina (297)
Smilov Laz (8)
Srednja Tušimlja (40)
Štitare (77)
Stradovo (19)
Sudsko Selo (87)
Tenkovo (89)
Trnava (694)
Tunovo (128)
Varevo (501)
Vever (18)
Vidovo (90)
Vitkoviće (30)
Vojkoviće (36)
Vojniće (115)
Vranovina (329)
Vučiniće (245)
Vučja Lokva (15)
Zabrđe (49)
Zlatare (12)
Žunjeviće (211)
Politics[edit]
Novi Pazar is governed by a city assembly composed of 47 councillors, a mayor and vice-mayor. After the last legislative election held in 2012, the local assembly is composed of the following groups:[30]
- European Novi Pazar - Rasim Ljajić SDP, SDPS (18)
Party of Democratic Action of Sandžak (11)- Bošnjačka demokratska zajednica Sandžaka - Muamer Zukorlić (10)
- Aleksandar Vučić - Srbija pobeđuje (5)
- Mirsad Đerlek - SNP (3)
Economy[edit]
Lying on crossroads between numerous old and new states, Novi Pazar has always been a strong trade center. Along with the trade, the city developed manufacturing tradition. During the 20th century, it became a center of textile industry.
Paradoxically, during the turbulent 1990s and, Novi Pazar prospered, even during the UN sanctions, boosted by the strong private initiative in textile industry. Jeans of Novi Pazar, first of forged trademarks, and later on its own labels, became famous throughout the region. However, during the relative economic prosperity in Serbia of the 2000s, the Novi Pazar economy collapsed, with demise of large textile combines in mismanaged privatization, and incoming competition from the import.
- Economic figures
The following table gives a preview of total number of employed people per their core activity (as of 2016):[31]
| Activity | Total |
|---|---|
| Agriculture, forestry and fishing | 76 |
| Mining | 80 |
| Processing industry | 4,001 |
| Distribution of power, gas and water | 220 |
| Distribution of water and water waste management | 351 |
| Construction | 1,547 |
| Wholesale and retail, repair | 3,653 |
| Traffic, storage and communication | 1,166 |
| Hotels and restaurants | 710 |
| Media and telecommunications | 226 |
| Finance and insurance | 214 |
| Property stock and charter | 6 |
| Professional, scientific, innovative and technical activities | 464 |
| Administrative and other services | 302 |
| Administration and social assurance | 1,348 |
| Education | 2,116 |
| Healthcare and social work | 1,643 |
| Art, leisure and recreation | 205 |
| Other services | 556 |
| Total | 18,863 |
Society and culture[edit]
Monuments[edit]
The old Serbian Orthodox monastery of Sopoćani, the foundation of St King Uroš I, built in the second half of the 13th century and located west of Novi Pazar, is a World Heritage Site since 1979 accompanying with Stari Ras (Old Ras), a medieval capital of the Serbian great župan Stefan Nemanja.[citation needed]
The city also houses the oldest intact church in Serbia and one of the oldest ones in the region which dates from the 9th-century, the Church of St Peter. The church's walls were defaced with graffiti on 6 April 2008. The police have not officially concluded why the incident occurred.[32]
On a hilltop overlooking Novi Pazar is the 12th century monastery of Đurđevi stupovi, long left in ruin, but recently restored and with a monastic community using it, with plate glass to keep out the weather and preserve the fine frescos. The main mosque of the city, the Altun-Alem Mosque, is the largest in this region of the Balkans and dates from 16th century.[citation needed] There are various other historic Ottoman buildings, such as the 17th-century Amir-agin Han, a 15th-century Hammam, and the 15th-century Turkish fortress (all gone but the walls, the site of which is now a walled park in the city centre).[citation needed]
Education[edit]

Faculty for Islamic studies in Novi Pazar
Novi Pazar is home to two universities, the International University of Novi Pazar and the State University of Novi Pazar.
Sport[edit]
The city's football club FK Novi Pazar was founded in 1928, under the name "FK Sandžak", which later changed to "FK Deževa". The club has played under its current name since 1962, when Deževa and another local football club, FK Ras, unified under this name. The club was a SFRJ amateur champion, and a member of the Yugoslav Second League. FK Novi Pazar qualified for a promotional play-off twice, but lost both times (to FK Sutjeska Nikšić in 1994, and to FK Sloboda Užice in 1995). FK Novi Pazar finally promoted to Serbian SuperLiga in 2011-12 season. FK Novi Pazar is the oldest second-league team in Serbia. Football is still an extremely popular sport in Novi Pazar and the city stadium is always full.
Volleyball clubs in the city are OK Novi Pazar (first league) and OK Koteks.
The Handball club is in the second league and used to have the name "Ras" but it was changed to RK Novi Pazar in 2004.
The Basketball club of the city is OKK Novi Pazar.
Famous athletes from the city include Turkish basketball national team player Mirsad Jahović Türkcan, former football player of Besiktas Sead Halilagić, handball-player Mirsad Terzić (who represents Bosnia and Herzegovina) and young football players Adem Ljajić, Ediz Bahtiyaroğlu, Armin Đerlek and alpinist Basar Čarovac who climbed all seven continents' highest peaks.
Gallery[edit]
Novi Pazar city center

Novi Pazar city center

Novi Pazar city center

Novi Pazar Mosque in the neighborhood

Novi Pazar City Stadium
Notable residents[edit]
Basar Čarovac, Mountaineer
Abdulah Gegić, former Partizan Belgrade football coach
Almir Gegić, football player
Aćif Hadžiahmetović, politician, mayor of Novi Pazar during Second World War
Sead Halilagić, former football player
Emina Jahović, pop singer
Tahir Efendi Jakova, Albanian poet
Adem Ljajić, FC Torino football player
Rasim Ljajić, Republic of Serbia Minister of Foreign and Domestic Trade and Telecommunications
Miljan Mutavdžić, footballer, former Serbian national team player
Laza Ristovski (1956-2007), Yugoslav keyboardist, member of Smak and Bijelo Dugme
Milunka Savić (1888–1973), the most-decorated female combatant in the entire history of warfare
Elma Sinanović, pop singer
Mirsad Jahović Türkcan, Turkish basketball player
Bajro Župić, former Partizan Belgrade football player
References[edit]
^ "Municipalities of Serbia, 2006". Statistical Office of Serbia. Retrieved 2010-11-28..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output .citation qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-maintdisplay:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ "2011 Census of Population, Households and Dwellings in the Republic of Serbia: Comparative Overview of the Number of Population in 1948, 1953, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991, 2002 and 2011, Data by settlements" (PDF). Statistical Office of Republic Of Serbia, Belgrade. 2014. ISBN 978-86-6161-109-4. Retrieved 2014-06-27.
^ abc "Попис становништва, домаћинстава и станова 2011. у Републици Србији" (PDF). stat.gov.rs. Republički zavod za statistiku. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
^ Ahrens, Geert-Hinrich. Diplomacy on the Edge: Containment of Ethnic Conflict and the Minorities Working Group of the Conferences on Yugoslavia. Woodrow Wilson Center Press. pp. 223–. ISBN 9780801885570. Retrieved 2 January 2013.
^ "bazaar". Retrieved 2007-02-17.
^ "Climate: Novi Pazar, Serbia". Climate-Data.org. Retrieved December 28, 2017.
^ Više autora, Novi Pazar i okolina, Beograd 1969.[page needed]
^ Norris, H. T. (1993). Islam in the Balkans: Religion and Society Between Europe and the Arab World. Hurst. pp. 49–. ISBN 9781850651673. Retrieved 2 January 2013.Novi Pazar, on the border of Kosovo, was founded by Isa Beg, a governor of Bosnia
^ Holger H., Richard F. Hamilton. The Origins of World War I. Cambridge University Press. p. 103. ISBN 9781107393868.
^ HALL, RICHARD C. (2002). The Balkan Wars 1912-1913: Prelude to the First World War Warfare and History. Routledge, 2002. ISBN 9781134583621.
^ N., M. (3 November 2016). "Zukorlić: Sa stokom reforme nemoguće". novosti.rs (in Serbian). Retrieved 17 February 2017.
^ "Zoran Đinđić dobija ulicu u Novom Pazaru". blic.rs (in Serbian). Tanjug. 12 March 2015. Retrieved 17 February 2017.
^ "2011 Census of Population, Households and Dwellings in the Republic of Serbia" (PDF). stat.gov.rs. Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia. Retrieved 11 January 2017.
^ "STANOVNIŠTVO". novipazar.rs (in Serbian). Archived from the original on 19 June 2014. Retrieved 13 July 2014.
^ "Number and the floor space of housing units" (PDF). stat.gov.rs (in Serbian). Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia. Retrieved 21 March 2018.
^ abc "Religion, Mother tongue, and Ethnicity" (PDF). stat.gov.rs (in Serbian). Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia. Retrieved 21 March 2018.
^ "Educational attainment, literacy and computer literacy" (PDF). stat.gov.rs (in Serbian). Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia. Retrieved 21 March 2018.
^ Hall, Richard C. (2002-01-04). The Balkan Wars 1912-1913: Prelude to the First World War. Taylor & Francis. p. 5. ISBN 9780203138052. Retrieved 2 January 2013.The Sandjak of Novi Pazar was a finger of the Ottoman province of Kosovo, which separated Montenegro from Serbia. The Sandjak of Novi Pazar had a mixed population of Albanians, Serbs, and Slavic-speaking Muslims.
^ Cohen, Philip J.; Riesman, David (1996). Serbia's Secret War: Propaganda and the Deceit of History. Texas A&M University Press. pp. 191–. ISBN 9780890967607. Retrieved 2 January 2013.Before World War II, about 10,500 Jews lived in Belgrade, about 350 in Nis, about 250 in Novi Pazar (Sandzak)
^ Mušović, Ejup (1979), Etnički procesi i ethnička struktura stanovništva Novog Pazara, Etnografski Institut, 1979, p.48
^ "Comparative Overview of the number of population in 1948, 1953, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991, 2002 and 2011" (PDF). stat.gov.rs. Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia. 2012. Retrieved 13 July 2014.
^ Stanković, Republika Srbija, Republički Zavod za Statistiku. (2004). Comparative survey of population 1948, 1953, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991 and 2002 : data by localities (in Serbian). Belgrade: Republički zavod za statistiku. ISBN 86-84433-14-9.
^ ab "UKUPNO STANOVNIŠTVO PO NARODNOSTI (1953)" (PDF). stat.gov.rs. Republički zavod za statistiku. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
^ "Knjiga III: Nacionalni sastav stanovništva FNR Jugoslavije (1961)" (PDF). stat.gov.rs (in Serbian). Republički zavod za statistiku. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
^ "Knjiga III: Nacionalni sastav stanovništva FNR Jugoslavije (1971)" (PDF). stat.gov.rs (in Serbian). Republički zavod za statistiku. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
^ ab "Nacionalni sastav stanovništva SFR Jugoslavije (1981)" (PDF). stat.gov.rs. Republički zavod za statistiku. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
^ ab "STANOVNIŠTVO PREMA NACIONALNOJ PRIPADNOSTI (1991)" (PDF). stat.gov.rs. Republički zavod za statistiku. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
^ ab "Popis stanovništva, domaćinstava i stanova u 2002" (PDF). stat.gov.rs (in Serbian). Republički zavod za statistiku. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
^ "UKUPNO STANOVNIŠTVO PO NARODNOSTI (1948)" (PDF). stat.gov.rs. Republički zavod za statistiku. Retrieved 25 December 2016.
^ "Skupština grada". Novipazar.rs. Archived from the original on 2012-09-04. Retrieved 2014-08-08.
^ "ОПШТИНЕ И РЕГИОНИ У РЕПУБЛИЦИ СРБИЈИ, 2017" (PDF). stat.gov.rs (in Serbian). Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia. Retrieved 20 February 2018.
^ "Oldest Orthodox church in Balkans (Serbian Orthodox Church) defaced". Spc.rs. Retrieved 8 August 2014.
External links[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Novi Pazar. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Novi Pazar. |
- Official website
Categories:
- Populated places in Raška District
- Sandžak
- Municipalities and cities of Šumadija and Western Serbia
- Novi Pazar
- Ottoman market towns
(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function()mw.config.set("wgPageParseReport":"limitreport":"cputime":"1.376","walltime":"1.758","ppvisitednodes":"value":8714,"limit":1000000,"ppgeneratednodes":"value":0,"limit":1500000,"postexpandincludesize":"value":245304,"limit":2097152,"templateargumentsize":"value":24718,"limit":2097152,"expansiondepth":"value":25,"limit":40,"expensivefunctioncount":"value":11,"limit":500,"unstrip-depth":"value":1,"limit":20,"unstrip-size":"value":98831,"limit":5000000,"entityaccesscount":"value":1,"limit":400,"timingprofile":["100.00% 1436.279 1 -total"," 25.96% 372.794 1 Template:Infobox_settlement"," 23.16% 332.656 1 Template:Reflist"," 17.72% 254.441 1 Template:Infobox"," 14.63% 210.158 21 Template:Cite_web"," 11.12% 159.741 9 Template:Cn"," 10.50% 150.789 10 Template:Fix"," 10.13% 145.447 1 Template:Lang-sr-cyr"," 7.45% 106.963 1 Template:Serbian_municipalities_2006"," 6.92% 99.440 6 Template:Navbox"],"scribunto":"limitreport-timeusage":"value":"0.656","limit":"10.000","limitreport-memusage":"value":23976931,"limit":52428800,"cachereport":"origin":"mw1284","timestamp":"20190315134415","ttl":2592000,"transientcontent":false);mw.config.set("wgBackendResponseTime":98,"wgHostname":"mw1246"););