Digestion
Digestion
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Digestive system | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | systema digestorium |
| MeSH | D004063 |
Anatomical terminology [edit on Wikidata] | |
Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into the blood stream. Digestion is a form of catabolism that is often divided into two processes based on how food is broken down: mechanical and chemical digestion. The term mechanical digestion refers to the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces which can subsequently be accessed by digestive enzymes. In chemical digestion, enzymes break down food into the small molecules the body can use.
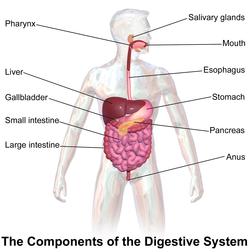
In the human digestive system, food enters the mouth and mechanical digestion of the food starts by the action of mastication (chewing), a form of mechanical digestion, and the wetting contact of saliva. Saliva, a liquid secreted by the salivary glands, contains salivary amylase, an enzyme which starts the digestion of starch in the food; the saliva also contains mucus, which lubricates the food, and hydrogen carbonate, which provides the ideal conditions of pH (alkaline) for amylase to work. After undergoing mastication and starch digestion, the food will be in the form of a small, round slurry mass called a bolus. It will then travel down the esophagus and into the stomach by the action of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach starts protein digestion. Gastric juice mainly contains hydrochloric acid and pepsin. It also contains rennin in case of infants and toddlers. As the first two chemicals may damage the stomach wall, mucus is secreted by the stomach, providing a slimy layer that acts as a shield against the damaging effects of the chemicals. At the same time protein digestion is occurring, mechanical mixing occurs by peristalsis, which is waves of muscular contractions that move along the stomach wall. This allows the mass of food to further mix with the digestive enzymes.
After some time (typically 1–2 hours in humans, 4–6 hours in dogs, 3–4 hours in house cats),[citation needed] the resulting thick liquid is called chyme. When the pyloric sphincter valve opens, chyme enters the duodenum where it mixes with digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile juice from the liver and then passes through the small intestine, in which digestion continues. When the chyme is fully digested, it is absorbed into the blood. 95% of absorption of nutrients occurs in the small intestine. Water and minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood in the colon (large intestine) where the pH is slightly acidic about 5.6 ~ 6.9. Some vitamins, such as biotin and vitamin K (K2MK7) produced by bacteria in the colon are also absorbed into the blood in the colon. Waste material is eliminated from the rectum during defecation.[1]
Contents
1 Digestive system
1.1 Secretion systems
1.1.1 Channel transport system
1.1.2 Molecular syringe
1.1.3 Conjugation machinery
1.1.4 Release of outer membrane vesicles
1.2 Gastrovascular cavity
1.3 Phagosome
1.4 Specialised organs and behaviours
1.4.1 Beaks
1.4.2 Tongue
1.4.3 Teeth
1.4.4 Crop
1.4.5 Abomasum
1.4.6 Specialised behaviours
1.5 In earthworms
2 Overview of vertebrate digestion
3 Human digestion process
3.1 Neural and biochemical control mechanisms
4 Breakdown into nutrients
4.1 Protein digestion
4.2 Fat digestion
4.3 Carbohydrate digestion
4.4 DNA and RNA digestion
5 Non-destructive digestion
6 Digestive hormones
7 Significance of pH
8 See also
9 References
10 External links
Digestive system
Digestive systems take many forms. There is a fundamental distinction between internal and external digestion. External digestion developed earlier in evolutionary history, and most fungi still rely on it.[2] In this process, enzymes are secreted into the environment surrounding the organism, where they break down an organic material, and some of the products diffuse back to the organism. Animals have a tube (gastrointestinal tract) in which internal digestion occurs, which is more efficient because more of the broken down products can be captured, and the internal chemical environment can be more efficiently controlled.[3]
Some organisms, including nearly all spiders, simply secrete biotoxins and digestive chemicals (e.g., enzymes) into the extracellular environment prior to ingestion of the consequent "soup". In others, once potential nutrients or food is inside the organism, digestion can be conducted to a vesicle or a sac-like structure, through a tube, or through several specialized organs aimed at making the absorption of nutrients more efficient.

Schematic drawing of bacterial conjugation. 1- Donor cell produces pilus. 2- Pilus attaches to recipient cell, bringing the two cells together. 3- The mobile plasmid is nicked and a single strand of DNA is transferred to the recipient cell. 4- Both cells recircularize their plasmids, synthesize second strands, and reproduce pili; both cells are now viable donors.
Secretion systems
Bacteria use several systems to obtain nutrients from other organisms in the environments.
Channel transport system
In a channel transupport system, several proteins form a contiguous channel traversing the inner and outer membranes of the bacteria. It is a simple system, which consists of only three protein subunits: the ABC protein, membrane fusion protein (MFP), and outer membrane protein (OMP)[specify]. This secretion system transports various molecules, from ions, drugs, to proteins of various sizes (20–900 kDa). The molecules secreted vary in size from the small Escherichia coli peptide colicin V, (10 kDa) to the Pseudomonas fluorescens cell adhesion protein LapA of 900 kDa.[4]
Molecular syringe
A type III secretion system means that a molecular syringe is used through which a bacterium (e.g. certain types of Salmonella, Shigella, Yersinia) can inject nutrients into protist cells. One such mechanism was first discovered in Y. pestis and showed that toxins could be injected directly from the bacterial cytoplasm into the cytoplasm of its host's cells rather than simply be secreted into the extracellular medium.[5]
Conjugation machinery
The conjugation machinery of some bacteria (and archaeal flagella) is capable of transporting both DNA and proteins. It was discovered in Agrobacterium tumefaciens, which uses this system to introduce the Ti plasmid and proteins into the host, which develops the crown gall (tumor).[6] The VirB complex of Agrobacterium tumefaciens is the prototypic system.[7]
The nitrogen fixing Rhizobia are an interesting case, wherein conjugative elements naturally engage in inter-kingdom conjugation. Such elements as the Agrobacterium Ti or Ri plasmids contain elements that can transfer to plant cells. Transferred genes enter the plant cell nucleus and effectively transform the plant cells into factories for the production of opines, which the bacteria use as carbon and energy sources. Infected plant cells form crown gall or root tumors. The Ti and Ri plasmids are thus endosymbionts of the bacteria, which are in turn endosymbionts (or parasites) of the infected plant.
The Ti and Ri plasmids are themselves conjugative. Ti and Ri transfer between bacteria uses an independent system (the tra, or transfer, operon) from that for inter-kingdom transfer (the vir, or virulence, operon). Such transfer creates virulent strains from previously avirulent Agrobacteria.
Release of outer membrane vesicles
In addition to the use of the multiprotein complexes listed above, Gram-negative bacteria possess another method for release of material: the formation of outer membrane vesicles.[8][9] Portions of the outer membrane pinch off, forming spherical structures made of a lipid bilayer enclosing periplasmic materials. Vesicles from a number of bacterial species have been found to contain virulence factors, some have immunomodulatory effects, and some can directly adhere to and intoxicate host cells. While release of vesicles has been demonstrated as a general response to stress conditions, the process of loading cargo proteins seems to be selective.[10]

Venus Flytrap (Dionaea muscipula) leaf
Gastrovascular cavity
The gastrovascular cavity functions as a stomach in both digestion and the distribution of nutrients to all parts of the body. Extracellular digestion takes place within this central cavity, which is lined with the gastrodermis, the internal layer of epithelium. This cavity has only one opening to the outside that functions as both a mouth and an anus: waste and undigested matter is excreted through the mouth/anus, which can be described as an incomplete gut.
In a plant such as the Venus Flytrap that can make its own food through photosynthesis, it does not eat and digest its prey for the traditional objectives of harvesting energy and carbon, but mines prey primarily for essential nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus in particular) that are in short supply in its boggy, acidic habitat.[11]

Trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica with ingested erythrocytes
Phagosome
A phagosome is a vacuole formed around a particle absorbed by phagocytosis. The vacuole is formed by the fusion of the cell membrane around the particle. A phagosome is a cellular compartment in which pathogenic microorganisms can be killed and digested. Phagosomes fuse with lysosomes in their maturation process, forming phagolysosomes. In humans, Entamoeba histolytica can phagocytose red blood cells.[12]
Specialised organs and behaviours
To aid in the digestion of their food animals evolved organs such as beaks, tongues, teeth, a crop, gizzard, and others.
.mw-parser-output .tmulti .thumbinnerdisplay:flex;flex-direction:column.mw-parser-output .tmulti .trowdisplay:flex;flex-direction:row;clear:left;flex-wrap:wrap;width:100%;box-sizing:border-box.mw-parser-output .tmulti .tsinglemargin:1px;float:left.mw-parser-output .tmulti .theaderclear:both;font-weight:bold;text-align:center;align-self:center;background-color:transparent;width:100%.mw-parser-output .tmulti .thumbcaptiontext-align:left;background-color:transparent.mw-parser-output .tmulti .text-align-lefttext-align:left.mw-parser-output .tmulti .text-align-righttext-align:right.mw-parser-output .tmulti .text-align-centertext-align:center@media all and (max-width:720px).mw-parser-output .tmulti .thumbinnerwidth:100%!important;box-sizing:border-box;max-width:none!important;align-items:center.mw-parser-output .tmulti .trowjustify-content:center.mw-parser-output .tmulti .tsinglefloat:none!important;max-width:100%!important;box-sizing:border-box;text-align:center.mw-parser-output .tmulti .thumbcaptiontext-align:center


Beaks
Birds have bony beaks that are specialised according to the bird's ecological niche. For example, macaws primarily eat seeds, nuts, and fruit, using their impressive beaks to open even the toughest seed. First they scratch a thin line with the sharp point of the beak, then they shear the seed open with the sides of the beak.
The mouth of the squid is equipped with a sharp horny beak mainly made of cross-linked proteins. It is used to kill and tear prey into manageable pieces. The beak is very robust, but does not contain any minerals, unlike the teeth and jaws of many other organisms, including marine species.[13] The beak is the only indigestible part of the squid.
Tongue
The tongue is skeletal muscle on the floor of the mouth that manipulates food for chewing (mastication) and swallowing (deglutition). It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva. The underside of the tongue is covered with a smooth mucous membrane. The tongue also has a touch sense for locating and positioning food particles that require further chewing. The tongue is utilized to roll food particles into a bolus before being transported down the esophagus through peristalsis.
The sublingual region underneath the front of the tongue is a location where the oral mucosa is very thin, and underlain by a plexus of veins. This is an ideal location for introducing certain medications to the body. The sublingual route takes advantage of the highly vascular quality of the oral cavity, and allows for the speedy application of medication into the cardiovascular system, bypassing the gastrointestinal tract.
Teeth
Teeth (singular tooth) are small whitish structures found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates that are used to tear, scrape, milk and chew food. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of tissues of varying density and hardness, such as enamel, dentine and cementum. Human teeth have a blood and nerve supply which enables proprioception. This is the ability of sensation when chewing, for example if we were to bite into something too hard for our teeth, such as a chipped plate mixed in food, our teeth send a message to our brain and we realise that it cannot be chewed, so we stop trying.
The shapes, sizes and numbers of types of animals' teeth are related to their diets. For example, herbivores have a number of molars which are used to grind plant matter, which is difficult to digest. Carnivores have canine teeth which are used to kill and tear meat.
Crop
A crop, or croup, is a thin-walled expanded portion of the alimentary tract used for the storage of food prior to digestion. In some birds it is an expanded, muscular pouch near the gullet or throat. In adult doves and pigeons, the crop can produce crop milk to feed newly hatched birds.[14]
Certain insects may have a crop or enlarged esophagus.

Rough illustration of a ruminant digestive system
Abomasum
Herbivores have evolved cecums (or an abomasum in the case of ruminants). Ruminants have a fore-stomach with four chambers. These are the rumen, reticulum, omasum, and abomasum. In the first two chambers, the rumen and the reticulum, the food is mixed with saliva and separates into layers of solid and liquid material. Solids clump together to form the cud (or bolus). The cud is then regurgitated, chewed slowly to completely mix it with saliva and to break down the particle size.
Fibre, especially cellulose and hemi-cellulose, is primarily broken down into the volatile fatty acids, acetic acid, propionic acid and butyric acid in these chambers (the reticulo-rumen) by microbes: (bacteria, protozoa, and fungi). In the omasum, water and many of the inorganic mineral elements are absorbed into the blood stream.
The abomasum is the fourth and final stomach compartment in ruminants. It is a close equivalent of a monogastric stomach (e.g., those in humans or pigs), and digesta is processed here in much the same way. It serves primarily as a site for acid hydrolysis of microbial and dietary protein, preparing these protein sources for further digestion and absorption in the small intestine. Digesta is finally moved into the small intestine, where the digestion and absorption of nutrients occurs. Microbes produced in the reticulo-rumen are also digested in the small intestine.

A flesh fly "blowing a bubble", possibly to concentrate its food by evaporating water
Specialised behaviours
Regurgitation has been mentioned above under abomasum and crop, referring to crop milk, a secretion from the lining of the crop of pigeons and doves with which the parents feed their young by regurgitation.[15]
Many sharks have the ability to turn their stomachs inside out and evert it out of their mouths in order to get rid of unwanted contents (perhaps developed as a way to reduce exposure to toxins).
Other animals, such as rabbits and rodents, practise coprophagia behaviours – eating specialised faeces in order to re-digest food, especially in the case of roughage. Capybara, rabbits, hamsters and other related species do not have a complex digestive system as do, for example, ruminants. Instead they extract more nutrition from grass by giving their food a second pass through the gut. Soft faecal pellets of partially digested food are excreted and generally consumed immediately. They also produce normal droppings, which are not eaten.
Young elephants, pandas, koalas, and hippos eat the faeces of their mother, probably to obtain the bacteria required to properly digest vegetation. When they are born, their intestines do not contain these bacteria (they are completely sterile). Without them, they would be unable to get any nutritional value from many plant components.
In earthworms
An earthworm's digestive system consists of a mouth, pharynx, esophagus, crop, gizzard, and intestine. The mouth is surrounded by strong lips, which act like a hand to grab pieces of dead grass, leaves, and weeds, with bits of soil to help chew. The lips break the food down into smaller pieces. In the pharynx, the food is lubricated by mucus secretions for easier passage. The esophagus adds calcium carbonate to neutralize the acids formed by food matter decay. Temporary storage occurs in the crop where food and calcium carbonate are mixed. The powerful muscles of the gizzard churn and mix the mass of food and dirt. When the churning is complete, the glands in the walls of the gizzard add enzymes to the thick paste, which helps chemically breakdown the organic matter. By peristalsis, the mixture is sent to the intestine where friendly bacteria continue chemical breakdown. This releases carbohydrates, protein, fat, and various vitamins and minerals for absorption into the body.
Overview of vertebrate digestion
In most vertebrates, digestion is a multistage process in the digestive system, starting from ingestion of raw materials, most often other organisms. Ingestion usually involves some type of mechanical and chemical processing. Digestion is separated into four steps:
Ingestion: placing food into the mouth (entry of food in the digestive system),- Mechanical and chemical breakdown: mastication and the mixing of the resulting bolus with water, acids, bile and enzymes in the stomach and intestine to break down complex molecules into simple structures,
- Absorption: of nutrients from the digestive system to the circulatory and lymphatic capillaries through osmosis, active transport, and diffusion, and
- Egestion (Excretion): Removal of undigested materials from the digestive tract through defecation.
Underlying the process is muscle movement throughout the system through swallowing and peristalsis. Each step in digestion requires energy, and thus imposes an "overhead charge" on the energy made available from absorbed substances. Differences in that overhead cost are important influences on lifestyle, behavior, and even physical structures. Examples may be seen in humans, who differ considerably from other hominids (lack of hair, smaller jaws and musculature, different dentition, length of intestines, cooking, etc.).
The major part of digestion takes place in the small intestine. The large intestine primarily serves as a site for fermentation of indigestible matter by gut bacteria and for resorption of water from digests before excretion.
In mammals, preparation for digestion begins with the cephalic phase in which saliva is produced in the mouth and digestive enzymes are produced in the stomach. Mechanical and chemical digestion begin in the mouth where food is chewed, and mixed with saliva to begin enzymatic processing of starches. The stomach continues to break food down mechanically and chemically through churning and mixing with both acids and enzymes. Absorption occurs in the stomach and gastrointestinal tract, and the process finishes with defecation.[1]