1984 United States presidential election in West Virginia
1984 United States presidential election in West Virginia
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
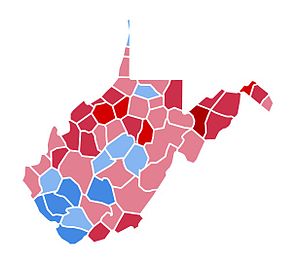 County Results Mondale—60-70% Mondale—50-60% Reagan—50-60% Reagan—60-70% Reagan—70-80% Reagan—80-90% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 1984 United States presidential election in West Virginia took place on November 6, 1984. All 50 states and the District of Columbia, were part of the 1984 United States presidential election. West Virginia voters chose 6 electors to the Electoral College, which selected the president and vice president of the United States.
West Virginia was won by incumbent United States President Ronald Reagan of California, who was running against former Vice President Walter Mondale of Minnesota. Reagan ran for a second time with incumbent Vice President and former C.I.A. Director George H. W. Bush of Texas, and Mondale ran with Representative Geraldine Ferraro of New York, the first major female candidate for the vice presidency.
Contents
1 Partisan background
2 Democratic platform
3 Republican platform
4 Republican victory
5 Results
6 See also
7 References
Partisan background[edit]
The presidential election of 1984 was a very partisan election for West Virginia, with over 99% of the electorate voting for either the Democratic or Republican parties, and only five parties appearing on the ballot.[1]
West Virginia weighed in for this election as 4% more Democratic than the national average.
Democratic platform[edit]
Walter Mondale accepted the Democratic nomination for presidency after pulling narrowly ahead of Senator Gary Hart of Colorado and Rev. Jesse Jackson of Illinois - his main contenders during what would be a very contentious[2] Democratic primary. During the campaign, Mondale was vocal about reduction of government spending, and, in particular, was vocal against heightened military spending on the nuclear arms race against the Soviet Union,[3] which was reaching its peak on both sides in the early 1980s.
Taking a (what was becoming the traditional liberal) stance on the social issues of the day, Mondale advocated for gun control, the right to choose regarding abortion, and strongly opposed the repeal of laws regarding institutionalized prayer in public schools. He also criticized Reagan for his economic marginalization of the poor, stating that Reagan's reelection campaign was "a happy talk campaign," not focused on the real issues at hand.[4]
A very significant political move during this election: the Democratic Party nominated Representative Geraldine Ferraro to run with Mondale as Vice-President. Ferraro is the first female candidate to receive such a nomination in United States history. She said in an interview at the 1984 Democratic National Convention that this action "opened a door which will never be closed again,"[5] speaking to the role of women in politics.
Republican platform[edit]

Reagan challenging Soviet General Secretary Mikhail Gorbachev to "tear down this wall!," from the Brandenburg Gate in June, 1987. Reagan's firm stance with the Soviet Union was an important contributor to his 1984 reelection.
| Elections in West Virginia | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||
Federal elections
| ||||||||||
State government
| ||||||||||
By 1984, Reagan was very popular with voters across the nation as the President who saw them out of the economic stagflation of the early and middle 1970's, and into a period of (relative) economic stability.[6]
The economic success seen under Reagan was politically accomplished (principally) in two ways. The first was initiation of deep tax cuts for the wealthy,[7] and the second was a wide-spectrum of tax cuts for crude oil production and refinement, namely, with the 1980 Windfall profits tax cuts.[8] These policies were augmented with a call for heightened military spending,[9] the cutting of social welfare programs for the poor,[10] and the increasing of taxes on those making less than $50,000 per year.[7] Collectively called "Reaganomics", these economic policies were established through several pieces of legislation passed between 1980 and 1987.
These new tax policies also arguably curbed several existing tax loopholes, preferences, and exceptions, but Reaganomics is typically remembered for its trickle down effect of taxing poor Americans more than rich ones. Reaganomics has (along with legislation passed under presidents George H. W. Bush and Bill Clinton) been criticized by many analysts as "setting the stage" for economic troubles in the United State after 2007, such as the Great Recession.[11]
Virtually unopposed during the Republican primaries, Reagan ran on a campaign of furthering his economic policies. Reagan vowed to continue his "war on drugs," passing sweeping legislation after the 1984 election in support of mandatory minimum sentences for drug possession.[12] Furthermore, taking a (what was becoming the traditional conservative) stance on the social issues of the day, Reagan strongly opposed legislation regarding comprehension of gay marriage, abortion, and (to a lesser extent) environmentalism,[13] regarding the final as simply being bad for business.
Republican victory[edit]
Reagan won the election in West Virginia with a decisive 11 point landslide. While West Virginia typically voted Democratic at the time, the election results in the state are also reflective of a nationwide reconsolidation of base for the Republican Party which took place through the 1980s; called by Reagan the "second American Revolution."[6] This was most evident during the 1984 election. West Virginia would not vote Republican again in a presidential election until 2000.
It is speculated that Mondale lost support with voters nearly immediately during the campaign, namely during his acceptance speech at the 1984 Democratic National Convention. There he stated that he intended to increase taxes. To quote Mondale, "By the end of my first term, I will reduce the Reagan budget deficit by two thirds. Let's tell the truth. It must be done, it must be done. Mr. Reagan will raise taxes, and so will I. He won't tell you. I just did."[4] Despite this claimed attempt at establishing truthfulness with the electorate, this promise to raise taxes badly eroded his chances in what had already begun as an uphill battle against the charismatic Ronald Reagan.
Reagan also enjoyed high levels of bipartisan support during the 1984 presidential election, both in West Virginia, and across the nation at large. Many registered Democrats who voted for Reagan (Reagan Democrats) stated that they had chosen to do so because they associated him with the economic recovery, because of his strong stance on national security issues with Russia, and because they considered the Democrats as "supporting American poor and minorities at the expense of the middle class."[13] These public opinion factors contributed to Reagan's 1984 landslide victory, in West Virginia and elsewhere.
Results[edit]
| United States presidential election in West Virginia, 1984 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Votes | Percentage | Electoral votes | |
Republican | Ronald Reagan | 405,483 | 55.11% | 6 | |
Democratic | Walter Mondale | 328,125 | 44.60% | 0 | |
America First | Bob Richards | 996 | 0.14% | 0 | |
Socialist Workers Party | Melvin Mason | 645 | 0.09% | 0 | |
New Alliance Party | Dennis Serrette | 493 | 0.07% | 0 | |
Totals | 735,742 | 100.00% | 6 | ||
See also[edit]
- Iran–Contra affair
- Nicaragua guerrilla war
- Presidency of Ronald Reagan
References[edit]
^ "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". Uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved 2013-11-11..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output .citation qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-maintdisplay:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ Kurt Andersen, "A Wild Ride to the End", Time, May 28, 1984
^ Trying to Win the Peace, by Even Thomas, Time, July 2, 1984
^ ab Mondale's Acceptance Speech, 1984, AllPolitics
^ Martin, Douglas (2011-03-27). "Geraldine A. Ferraro, First Woman on Major Party Ticket, Dies at 75". The New York Times. pp. A1. Retrieved November 5, 2013.
^ ab Raines, Howell (November 7, 1984). "Reagan Wins By a Landslide, Sweeping at Least 48 States; G.O.P. Gains Strength in House". The New York Times. Retrieved November 11, 2013.
^ ab "U.S. Federal Individual Income Tax Rates History, 1913–2011 (Nominal and Inflation-Adjusted Brackets)". Tax Foundation. September 9, 2011. Archived from the original on January 16, 2013. Retrieved November 10, 2013.
^ Joseph J. Thorndike (Nov 10, 2005). "Historical Perspective: The Windfall Profit Tax". Retrieved November 11, 2013.
^ Historical tables, Budget of the United States Government Archived 2012-04-17 at the Wayback Machine, 2013, table 6.1.
^ Niskanen, William A. (1992). "Reaganomics". In David R. Henderson. Concise Encyclopedia of Economics (1st ed.). Library of Economics and Liberty.
OCLC 317650570, 50016270, 163149563
^ Jerry Lanson (2008-11-06). "A historic victory. A changed nation. Now, can Obama deliver?". Christian Science Monitor. Retrieved 2013-11-02.
^ Alexander, Michelle (2010). The New Jim Crow. New York: The New Press. p. 5. ISBN 978-1595581037.
^ ab Prendergast, William B. (1999). The Catholic vote in American politics. Washington DC: Georgetown University Press. pp. 186, 191–193. ISBN 0-87840-724-3.
Categories:
- 1984 United States presidential election by state
- United States presidential elections in West Virginia
- 1984 West Virginia elections
(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function()mw.config.set("wgPageParseReport":"limitreport":"cputime":"0.548","walltime":"0.709","ppvisitednodes":"value":4596,"limit":1000000,"ppgeneratednodes":"value":0,"limit":1500000,"postexpandincludesize":"value":154241,"limit":2097152,"templateargumentsize":"value":9738,"limit":2097152,"expansiondepth":"value":15,"limit":40,"expensivefunctioncount":"value":6,"limit":500,"unstrip-depth":"value":1,"limit":20,"unstrip-size":"value":32402,"limit":5000000,"entityaccesscount":"value":0,"limit":400,"timingprofile":["100.00% 541.300 1 -total"," 43.31% 234.438 1 Template:Infobox_election"," 36.84% 199.398 1 Template:Reflist"," 32.53% 176.090 1 Template:Infobox"," 20.80% 112.610 4 Template:Cite_web"," 15.68% 84.868 3 Template:Infobox_election/row"," 7.00% 37.907 1 Template:ElectionsWV"," 6.00% 32.485 1 Template:Sidebar_with_collapsible_lists"," 4.86% 26.293 1 Template:Main"," 3.56% 19.248 1 Template:Max"],"scribunto":"limitreport-timeusage":"value":"0.173","limit":"10.000","limitreport-memusage":"value":4732549,"limit":52428800,"cachereport":"origin":"mw1273","timestamp":"20190301215930","ttl":2592000,"transientcontent":false););"@context":"https://schema.org","@type":"Article","name":"1984 United States presidential election in West Virginia","url":"https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/1984_United_States_presidential_election_in_West_Virginia","sameAs":"http://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q17016866","mainEntity":"http://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q17016866","author":"@type":"Organization","name":"Contributors to Wikimedia projects","publisher":"@type":"Organization","name":"Wikimedia Foundation, Inc.","logo":"@type":"ImageObject","url":"https://www.wikimedia.org/static/images/wmf-hor-googpub.png","datePublished":"2013-11-30T05:59:53Z","dateModified":"2019-02-13T13:30:22Z","image":"https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/83/President_Reagan_1985_closeup.jpg"(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function()mw.config.set("wgBackendResponseTime":132,"wgHostname":"mw1269"););




